Combinatorial optimization learning for backhauling in B5G/6G wireless networks
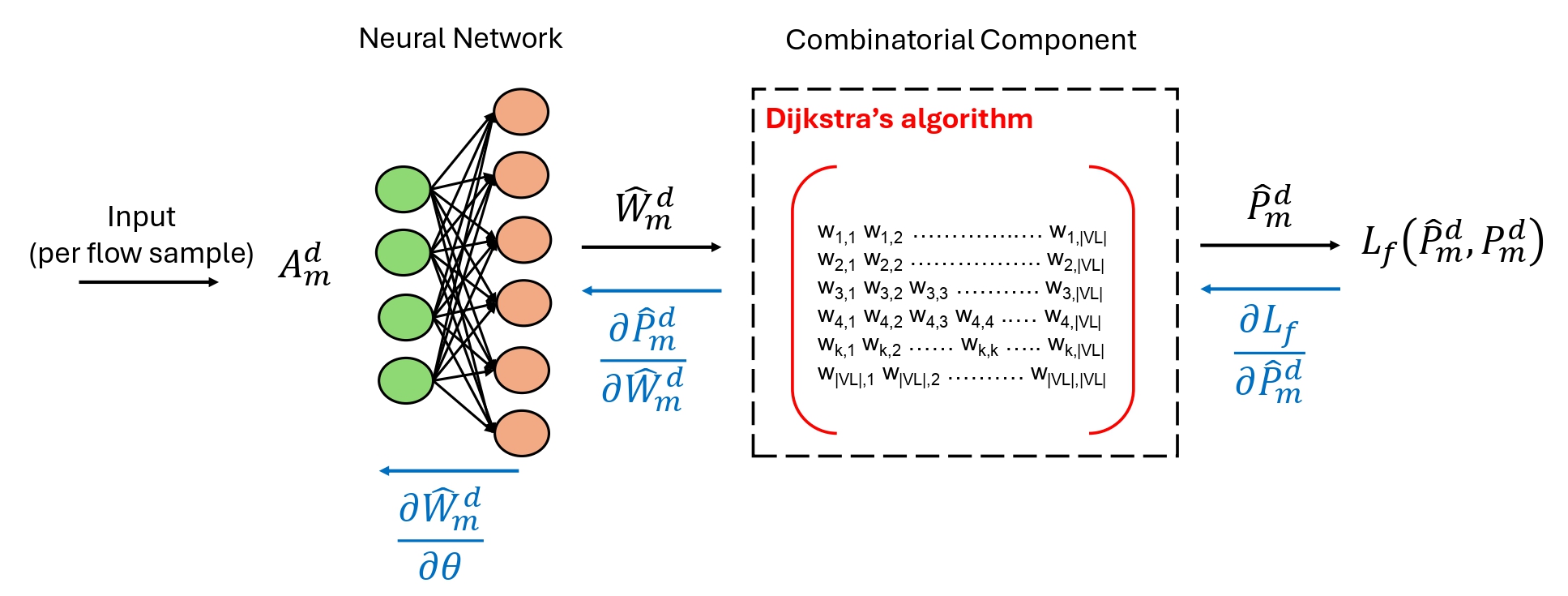
The UAV-assisted wireless backhauling is formulated as a multi-hop multi-commodity flow optimization problem, which is a mixed integer linear programming (MILP) problem with NP-hardness. Achieving energy-efficiency is a complex interplay between how many source UAVs and relay UAVs should be deployed, their locations, and the amount of traffic to be backhauled by the UAVs to the macro-base station. We tackle this problem in a “smart way” by proposing a combinatorial optimization learning approach (COLA) that integrates a combinatorial algorithm into a neural network to quickly and effectively approximate the solution to the MILP problem. First, the neural network predicts the “magic” link weights given the application-level inputs. The link weights are then used by a simple Dijkstra’s algorithm to find the shortest paths for the multi-commodity flows. Our work offer clear insights into how and why COLA outperforms other ML techniques, thus making COLA a viable approach for solving complex wireless network optimization problems.
Cite: O. T. Ajayi, S. Wang and Y. Cheng, “COLA: Combinatorial Optimization Learning Approach for Energy-Efficient Backhauling in UAV-Assisted B5G/6G Wireless Networks,” in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3622156.
